A Closer Look: The Science Behind Our Sterile Medical Disposables
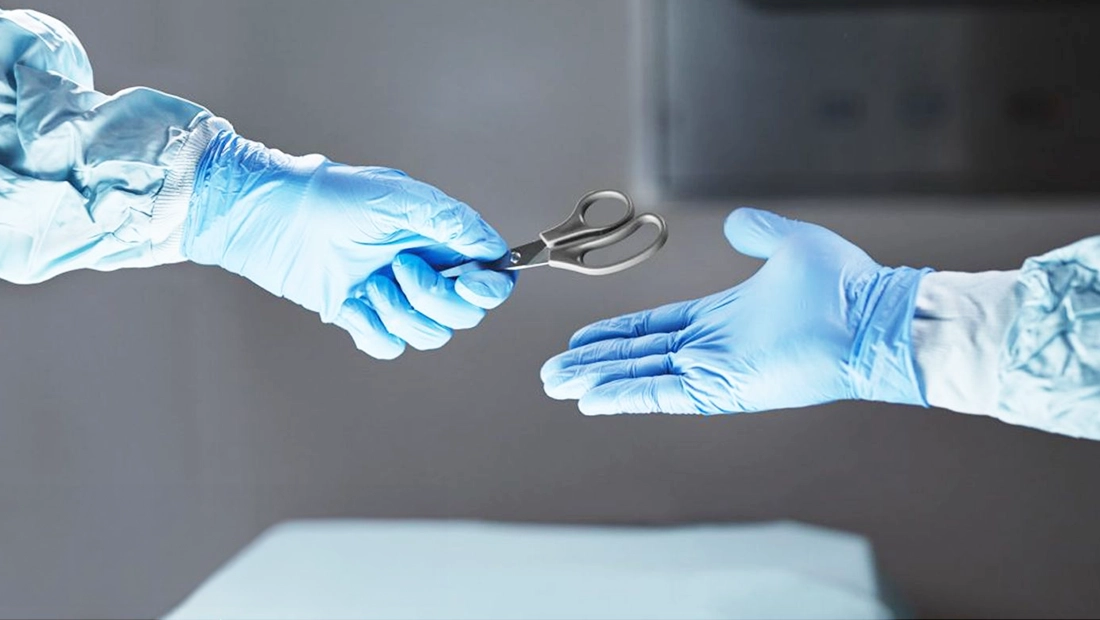
The medical disposable manufacturing sector plays a critical role in healthcare by producing items for one-time use that are designed to be sterile, which helps minimize the risk of infection. The items include syringes, gloves, face masks, and surgical instruments. Sterile disposables are essential in preventing cross-contamination in medical settings and ensuring that high hygiene standards are maintained. By using these disposables, which are manufactured in strict accordance with GMP regulations, healthcare professionals can deliver safer care, resulting in significantly reduced occurrence of healthcare-associated infections.
Materials Science
Medical disposables science revolves around selecting materials that are biocompatible, durable, and amenable to sterilization processes without failure. Frequently leveraged materials — medical-grade plastics, latex, nitrile, non-woven fabrics — all share inert character, allowing them to resist contamination from bacteria, viruses, etc. Plus, they can maintain their performance and integrity despite exposure to sterilization processes, such as autoclaving, radiation, or chemical sterilants, which ensures they remain safe and effective for medical use.
Sterilization Techniques

1. Ethylene Oxide Gas (EtO):
Key Feature: Sterility in medical products
How it Works: EtO gas is able to penetrate packages and products to disrupt the DNA of microorganisms – which prevents them from reproducing.
Suitability: Ideal for heat-sensitive sterile medical disposals like devices with plastic components or electronic parts.
2. Gamma Radiation:
Key Feature: Sterile medical disposables
How it Works: High-energy photons are used to break the DNA strands of microorganisms, so they are non-viable.
Suitability: Single-use medical disposables like syringes and surgical gloves — effective for both heat-sensitive and non-heat-sensitive products.
3. Steam Autoclaving:
Key Feature: Sterility in medical products
How it Works: Items are exposed to high temperature steam under pressure — killing microorganisms by denaturation of proteins.
Suitability: Best for heat-resistant items like surgical instruments and reusable glassware.
4. Electron Beam Sterilization
Key Feature: Sterile medical disposables
How it works: A high energy electron beam is directed to the product causing ionization of microbial DNA.
Suitability: Fast; Effective for a broad range of products; particularly suitable for bulk processing of low-density items, and products and materials that are sensitive to heat and humidity.
Regulatory Standards
Medical disposables technology is inundated with rules and regulations to ensure the products that are used in healthcare settings are safe and effective. Top organizations, like the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization), handle the oversight of this environment.
The FDA is the final authority in the U.S., evaluating and approving medical disposables before they can be marketed, ensuring that they meet very strict safety and performance standards. This includes a comprehensive evaluation of the materials used, sterilization processes and the disposables’ design and overall functionality.
On a global level, the ISO sets international standards for quality management and product safety, encompassing ISO 13485 which is specifically tailored to medical device manufacturers’ quality management systems. Adhering to ISO standards is often mandatory for selling medical disposables in the international marketplace, which ensures a very high level of quality and safety no matter where the products are sold.
Innovations in Sterilization Technology
 Two recent advances in medical disposables technology are found in the area of sterilization. One is the use of low-temperature plasma sterilization. Operating at a much lower temperature than traditional methods, this form of sterilization greatly reduces energy consumption and diminishes the chance of thermal damage to delicate medical devices. The other is peracetic acid sterilization. It presents a very effective, very fast sterilization process at a lower environmental price, for it eventually breaks down into its components non-toxic substances. Both represent a growing trend in the industry to create eco-friendly ways to enhance the safety and life span of medical disposables.
Two recent advances in medical disposables technology are found in the area of sterilization. One is the use of low-temperature plasma sterilization. Operating at a much lower temperature than traditional methods, this form of sterilization greatly reduces energy consumption and diminishes the chance of thermal damage to delicate medical devices. The other is peracetic acid sterilization. It presents a very effective, very fast sterilization process at a lower environmental price, for it eventually breaks down into its components non-toxic substances. Both represent a growing trend in the industry to create eco-friendly ways to enhance the safety and life span of medical disposables.
Packaging and Storage
The sterility of a medical product will entirely depend upon the integrity of its packaging, preventing physical, chemical, and microbial contamination, as the video demonstrates.
More recent packaging for advanced sterile medical disposables goes even further with multi-layer barriers to ensure a sterile barrier against microorganisms and particulates.
One innovative recent evolution in sterility in a medical product is self-sealing packages with a built-in indicator to change color when the package is fully sterilized for better safety and compliance, as the video notes.
That is especially important because disposable medical devices and medical disposables have become so advanced that some now have smart packaging with RFID tags, to allow for simple over-the-air tracking and management of inventory, while maintaining sterility to the point of use.
There have also been some material developments in sterile medical products packaging, with one trend being that more products may come in biodegradable and recyclable materials, and packaging in general being made from that, to reduce the environmental footprint and get rid of any material that could be not just a physical, but a chemical or biological contaminant, while keeping a sterile medical device sterile.
Finally, a bit part of the packaging of sterile medical disposables today is also making it tamper-evident, so if the product does somehow become non-sterile, that is very clear, and it does not get used by mistake: An example shows distinctive sterile medical disposables packaging tape with which it is very obvious to just about anyone who has seen any in a laboratory, operating room of a sterile processing area that it has been compromised.
Environmental Considerations
Manufacturing of medical disposables is on the fast track to environmental responsibility, with many innovations being driven by the need for sustainability. Much of this comes from product material advancements that are producing items that are degradable, for example. That means these materials can be broken down into its constituent parts without posing any environmental risk, such as plastic water bottles that break down into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass.
The waste footprint of disposable medical products is huge, so the medical industry is scrambling to cut it. As well as making them out of degradable materials, recyclable medical disposables are also being developed. Material is stripped from used disposables, broken down into base units, and put back into service. There are many hurdles to clear – not least that recycled items are not certified for all the uses virgin material is used for – but given the anti-disposable culture that is developing, it is likely a strong market will emerge to collect and recycle disposables.
Others fear this is greenwash, simply slowing the addition of medical waste to the nearly 2 million tons created by medical facilities yearly. Whether enacted half-heartedly or wholeheartedly, these devel
Future Trends
Smart technologies including RFID and sensors are expected to transform sterile medical disposables. These allow the real-time tracking of the sterilization process, ensuring compliance and integrity of the disposable. Meanwhile, medical disposable science is expected to benefit from the application of nanotechnology which is likely to result in surfaces that are inherently antimicrobial. Giving disposables a new level of infection protection. These changes will not only impact the safety of medical disposables but also make healthcare practices more efficient and sustainable.
Conclusion
“Innovation saves lives” rightly points out the life-saving potential of medical disposables technology and, at https://www.psidispo.com/ the life-changing impact on patient care of improvements to safety, efficiency and sterility in materials science, sterilization technology, regulatory standards and packaging that are constantly being driven forward. But, as the pace of smart technology and nano-technology in medical disposables shows, it is the science itself that is the truly critical factor – surely that was the respiratory innovation of the latter 20th century and who could not consider that the continued respiratory innovation now and into the future is the truly critical factor.
For additional insight into continued research and innovation in this area, visit https://www.psidispo.com/ regularly – and join us in driving forward the future of medical disposables technology.
Innovation saves lives; let’s innovate for a healthier tomorrow.