Five Approaches to Managing Waste Disposal
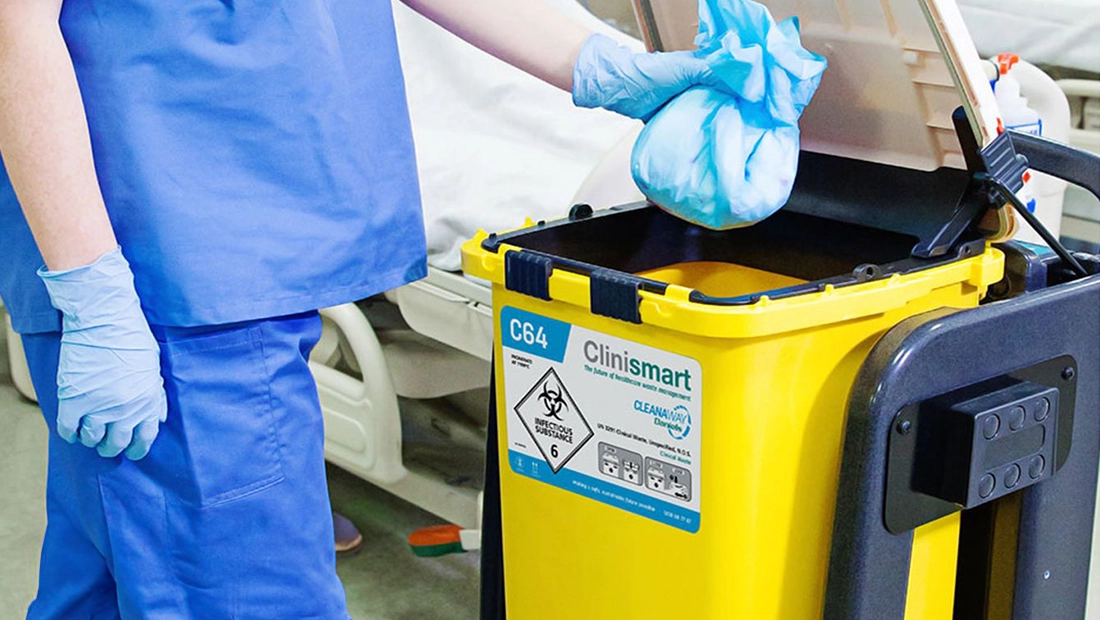
Waste management plays a critical role in ensuring environmental preservation and public health protection. Safe healthcare waste disposal is key in preventing the transmission of infections and diseases, ensuring that medical waste is appropriately handled and destroyed. Environmental waste management pertains to the wider realm of waste by focusing on reducing pollution and saving natural resources. However, the dramatic increase in global waste generation presents substantial hurdles. This upsurge is inundating existing waste management systems, leading to environmental degradation and health risks. Overcoming these challenges calls for innovative strategies and worldwide collaboration to ensure the sustainability of our planet and the health of all communities.
Recycling and Composting

Recycling
Waste disposal approaches Recycling – It is critical for effective recycling programs to separate materials like glass, paper, and certain types of plastics.
Reduction in landfill use – By diverting recyclable materials from landfills, we reduce the amount of waste being sent to landfills. This helps us conserve space and ensures that the lifespan of landfills is extended.
Resource conservation – By recycling, natural resources can be conserved. For example, recycling paper saves trees and both metals and glass can be recycled to avoid the need for raw material production.
Energy savings – Manufacturing from recycled materials often uses less energy than products made from new materials. This results in significant energy savings.
Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions – Reduced energy consumption leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Generally, the recycling process itself produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions than extractions and processing of raw materials.
Supports circular economy – By recycling, we support a circular economy. In the circular economy, materials are reused and recycled continually, which reduces the need for new resources and lessens environmental impacts.
Composting
- Waste Management Strategies: Composting – Converting organic waste, such as food scraps and yard waste, into compost is a key strategy.
- Soil Enrichment – Compost adds essential nutrients to soil, improving its quality and fertility, which benefits plant growth and agricultural productivity.
- Moisture Retention – When made part of the soil, compost can increase its water-holding capacity, reducing the need for watering and enhancing resistance to drought.
- Reduces Methane Emissions – By composting instead of sending organic waste to landfills, we reduce greenhouse gas emissions, especially methane, which is 25-percent more potent a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide and a significant contributor to climate change.
- Waste Volume Reduction – Composting decreases the volume of waste that is sent to landfills, which puts less pressure on waste management systems and keeps landfills open longer.
- Promotes Biodiversity – Healthy soils, enriched by compost, can support a much wider range of plant life and, thus, the animal and insect life those plants support, promoting biodiversity.
- Natural Pesticide – Compost can reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, leading to the establishment of healthier ecosystems and a reduced threat of those chemicals running off into our water sources.
Waste-to-Energy (WtE) technologies
Protocols for the management of medical waste disposal often include Waste-to-Energy (WtE) processes such as incineration and anaerobic digestion in environmental waste management strategies. WtE involves the conversion of waste materials, which generate electricity, heat, and/or fuel, and can be burned to generate electricity, heat, and/or fuel or broken down through the natural process of decay to produce biogas and nutrient-rich digested by the action of naturally occurring microorganisms in the absence of oxygen. By-products from WtE processes offer two benefits: the significant reduction of the volume of waste to be landfilled; and the production of a renewable source of energy that can contribute to the nation’s energy needs, help to alleviate the strain on the public utilities, and provide a more sustainable way to manage waste.
Waste-to-energy facilities, however, are equipped with several air pollution control technologies to reduce the release of potentially harmful emissions to the atmosphere, making the potential release of any harmful by-products from medical waste treatment unlikely. For example, the combustion of medical waste produces upstream and exhaust air monitors that display and document flows and temperatures every second, so that systems can detect leaks, malfunction, and certain diseases to ensure that emission levels are safely maintained.
Landfilling With Innovation
Modern landfill technology has come a long way and is well-equipped to handle safe healthcare waste disposal. Today, all landfills are required to have methane capture systems that collect harmful gases and transform them into a valuable energy source. What this means is that these harmful greenhouse gases are harvested and turned into usable energy which benefits us all. Landfills also have leachate management systems that ensure that any liquid waste does not leach out of the landfill and contaminate the groundwater. These landfills are incredibly engineered works that are essential for waste management as they keep our hazardous healthcare waste from affecting us or our environment. However, it is still very important that we all try to reduce the amount of waste we create to reduce the amount that goes into these landfills. Our waste reduction and recycling efforts can go a long way to reducing the environmental impact of waste disposal and keeping our valuable and limited natural resources.
Reduction and Reuse Strategies
 Waste disposal approaches should prioritize reducing the generation of waste in the first place. This is accomplished by minimizing packaging materials and encouraging the development of products that are longer-lasting. This approach not only lightens the burden on waste management systems, but it also helps move the way that we produce waste and use resources into a more sustainable and environmentally friendly direction.
Waste disposal approaches should prioritize reducing the generation of waste in the first place. This is accomplished by minimizing packaging materials and encouraging the development of products that are longer-lasting. This approach not only lightens the burden on waste management systems, but it also helps move the way that we produce waste and use resources into a more sustainable and environmentally friendly direction.
- Environmental Conservation: Reuse programs significantly reduce waste, conserving natural resources and minimizing environmental pollution.
- Economic Savings: Consumers save money by purchasing used goods at thrift stores or using repair services to extend product life.
- Waste Reduction: Extending the lifespan of goods through repair and reuse directly reduces the volume of waste destined for landfills.
- Community Engagement: Reuse initiatives often foster community involvement and awareness about sustainable living practices.
- Resource Efficiency: Product-sharing platforms maximize the utility of goods, ensuring they are used to their full potential rather than being discarded prematurely.
- Support for Non-Profits: Many thrift stores are operated by non-profit organizations, providing financial support for various social causes.
Policy and Education
Government policy and regulation are central to the governance necessary for effective waste management strategies, including healthcare waste disposal. Bans on single-use plastics and other disposable items dramatically reduce the volume of waste that disposal systems must manage and the impact of plastic on our environment. Incentives for recycling programs, both among the general public and for businesses, enhance overall recycling rates. Existing regulations to reduce waste, and to encourage sustainable materials management, make it clear that industries will need to adopt these practices. Collectively, they validate the responsible disposal of healthcare waste and support a society-wide culture of sustainability and environmental stewardship.
- Promotes Safe Practices: Public education ensures proper handling and disposal of medical waste, protecting community health and the environment.
- Reduces Improper Disposal: Awareness campaigns inform about the dangers of improper medical waste disposal, encouraging correct practices.
- Encourages Participation: Educating the public on medical waste disposal programs increases community involvement and compliance.
- Fosters Sustainability: Awareness initiatives highlight the role of sustainable practices in medical waste management, contributing to environmental conservation.
- Shifts Consumer Behavior: Education campaigns can lead to more environmentally conscious decisions, reducing waste generation in healthcare and beyond.
Conclusion
Addressing the complex challenge of waste disposal requires a multifaceted approach, integrating various waste management strategies to effectively reduce, reuse, recycle, and recover resources. Individuals, communities, and governments must collaborate to implement sustainable waste management solutions, as detailed at PSIDispo. These efforts are crucial not only for protecting our environment from pollution and degradation but also for conserving precious resources for future generations. Let’s unite in adopting and advocating for comprehensive waste management practices that ensure the well-being of our planet. Act now, get involved, and contribute to a sustainable future. Your actions today will pave the way for a healthier tomorrow.